What is a Silt Fence and Why It’s Essential for Erosion Control?
Erosion control is a critical aspect of maintaining the stability of construction sites, agricultural land, and areas near water bodies. Without proper measures, soil erosion can lead to significant environmental damage, infrastructure issues, and costly repairs. One of the most effective and widely used tools for controlling erosion and sediment runoff is the silt fence.
In this blog, we’ll explore what a silt fence is, how it works, and why it is essential for erosion control in various projects.
What is a Silt Fence?
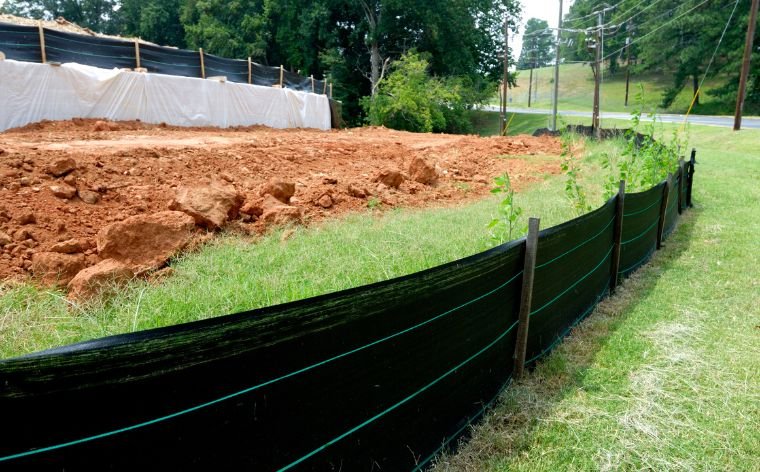
A silt fence is a temporary barrier made from woven geotextile fabric that is used to control sediment runoff and prevent soil erosion. These fences are typically installed around construction sites, agricultural fields, and areas prone to erosion to keep soil from washing away during rain or heavy water flow.
Silt fences are constructed by attaching the fabric to wooden or metal posts driven into the ground. The fabric itself is durable yet porous, allowing water to pass through while trapping soil and sediment particles. This simple but effective design makes silt fences an essential tool in preventing sediment pollution and controlling erosion.
They are commonly used:
- On construction sites to prevent soil loss during excavation or earth-moving activities.
- In agricultural settings where tilled soil is susceptible to erosion.
- Near water bodies to keep sediment from contaminating rivers, lakes, and streams.
How Does a Silt Fence Work?
The core function of a silt fence is to slow down the flow of water while trapping sediment. When water, especially during heavy rain or storms, rushes over bare soil, it picks up loose particles that can quickly become runoff. If left unchecked, this sediment-filled runoff can flow into nearby waterways, causing contamination and erosion.
A silt fence works by:
- Filtering the runoff: The woven fabric allows water to pass through but captures larger particles, such as soil, debris, and sediment.
- Slowing the flow: By creating a barrier, the silt fence reduces the velocity of water, which allows the sediment to settle before the water moves past the fence.
- Retaining sediment: As the water passes through the fence, the sediment is retained behind it, reducing erosion and preventing sediment from entering storm drains or natural waterways.
This process not only preserves the topsoil but also protects local ecosystems from harmful pollutants.
The Importance of Silt Fences for Erosion Control
Prevents Soil Loss
Soil is one of the most valuable natural resources, and its loss due to erosion can have long-term consequences. Silt fences are an excellent solution for keeping soil in place, especially in construction zones where the ground has been disturbed. By preventing soil from washing away, silt fences help maintain the integrity of the landscape and avoid the costly restoration of damaged areas.
Protects Waterways and Ecosystems
One of the most significant impacts of uncontrolled sediment runoff is waterway pollution. When sediment enters rivers, lakes, or streams, it can cloud the water and negatively affect aquatic ecosystems. Suspended sediments can smother fish habitats, disrupt aquatic plant life, and carry pollutants like pesticides and heavy metals. Silt fences act as a first line of defense, ensuring that these sediments are trapped before they can harm nearby water bodies.
Reduces Infrastructure Damage
Uncontrolled water and sediment runoff can also cause substantial damage to infrastructure. Flooded roads, clogged storm drains, and damaged foundations are just a few examples of how erosion can create costly issues. Installing silt fences in the right locations helps mitigate these risks by controlling the flow of water and keeping sediment where it belongs, thus preventing damage to surrounding structures.
Regulations and Compliance
Erosion control is not just about protecting the environment—it’s also about staying compliant with local, state, and federal regulations. In many regions, the installation of silt fences is a requirement for certain construction or landscaping projects. Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforce erosion control measures, especially on large construction sites where the risk of sediment runoff is high.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, project delays, or additional remediation costs. Therefore, it is essential to install silt fences according to the guidelines and ensure that they are properly maintained throughout the duration of the project.
Types of Silt Fences and Their Applications
Standard Silt Fences
Standard silt fences are suitable for small to medium-sized projects, such as residential construction sites or landscaping. They are relatively easy to install and provide effective sediment control in areas with moderate runoff.
Reinforced Silt Fences
In areas with more challenging environments, such as steep slopes or places prone to heavy runoff, reinforced silt fences provide additional support. These fences use stronger materials and are often installed with additional supports to ensure they can withstand higher water flow and sediment loads.
Wire-Backed Silt Fences
Wire-backed silt fences are used in areas with heavy sediment loads or where the fence will face significant pressure from water flow. The addition of a wire mesh backing provides extra strength and durability, ensuring the fence remains effective even under harsh conditions.
How to Install a Silt Fence Properly
Installing a silt fence properly is crucial for its effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Site Preparation: Clear the area of any debris, rocks, or vegetation. Make sure the soil is relatively smooth before installation.
- Dig a Trench: Dig a small trench (around 6 inches deep) along the path where the silt fence will be installed. This ensures that the bottom of the fabric is securely buried to prevent sediment from escaping underneath.
- Install the Fence Posts: Place the fence posts at regular intervals, typically 6 to 10 feet apart, depending on the terrain. The posts should be driven into the ground to a depth that ensures stability.
- Attach the Fabric: Secure the geotextile fabric to the posts, making sure the bottom of the fabric is buried in the trench. Stretch the fabric tightly to avoid sagging.
- Backfill the Trench: After the fence is in place, backfill the trench with soil and compact it to hold the fabric in place.
Maintenance and Monitoring of Silt Fences
Once a silt fence is installed, regular maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness. Inspect the fence periodically, especially after heavy rain or storms, to check for any signs of damage or displacement. Look for areas where the fabric may have torn or where sediment has accumulated excessively.
Replace or repair damaged sections immediately to avoid losing the effectiveness of the erosion control system. Additionally, when the project is complete, remove the silt fence and dispose of the materials properly, ensuring no leftover debris is left behind.
Conclusion
Silt fences are a simple yet highly effective solution for controlling erosion and protecting the environment. Whether you’re managing a construction site, an agricultural project, or simply working to preserve the natural landscape, a silt fence can provide essential protection against soil loss and sediment pollution. By preventing runoff from contaminating waterways and reducing the risk of infrastructure damage, silt fences play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance and regulatory compliance.